Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to chronic inflammation and damage. These conditions affect millions of people worldwide and can target various organs and systems, causing a wide range of symptoms and complications. In this in-depth article, we will explore the underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, common types, diagnoses, and effective strategies for managing and improving the quality of life for those living with these conditions.
The Immune System and Autoimmunity
The immune system is our body’s defense mechanism against harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. However, in autoimmune diseases, the immune system becomes dysfunctional and starts attacking healthy tissues, mistaking them for foreign substances. This process leads to persistent inflammation and tissue damage, which can be detrimental to overall health.
Common Types of Autoimmune Diseases
There are over 80 known autoimmune diseases, each affecting specific organs or systems in the body. Some common autoimmune diseases include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Which affects the joints and causes pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Affects multiple organs, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and heart.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Affects the central nervous system, leading to problems with balance, coordination, and vision.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Attacks the thyroid gland, causing an underactive thyroid.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which affect the digestive tract.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging, as their symptoms often overlap with other conditions. Medical history, physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies are commonly used to aid in diagnosis. Early detection is crucial to prevent further damage and improve treatment outcomes.
While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, treatments aim to suppress the overactive immune response, reduce inflammation, and manage symptoms. Medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications are commonly used to control autoimmune diseases and improve the patient’s quality of life.

Lifestyle Modifications for Autoimmune Management
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen autoimmune symptoms. Engage in relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, to manage stress levels.
- Balanced Diet: A nutrient-rich diet can support immune function and reduce inflammation. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats in your meals.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Choose exercises that are suitable for your condition and fitness level.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough restorative sleep is essential for immune function and overall health.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid factors that worsen your symptoms. This may include certain foods, environmental triggers, or excessive physical exertion.
The Role of Diet in Autoimmune Diseases
While diet alone cannot cure autoimmune diseases, it can significantly influence the body’s inflammatory response and immune function. Certain foods can trigger inflammation and exacerbate symptoms, while others may have anti-inflammatory properties, offering relief to individuals with autoimmune conditions. Understanding the impact of different nutrients on the immune system can empower patients to make informed dietary choices that complement their treatment plans.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
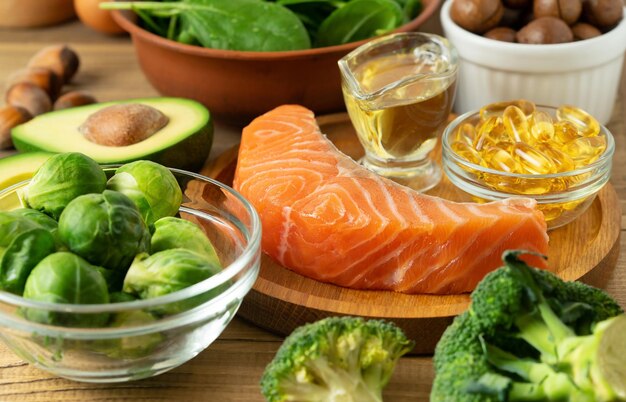
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into the diet can help manage symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases. Some examples of anti-inflammatory foods include:
Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health.

Berries: Packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, berries can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
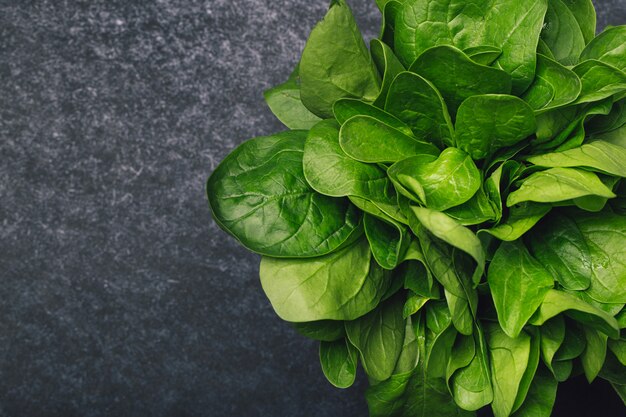
Leafy Greens: Kale, spinach, and other leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall health.

Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound with numerous health benefits.
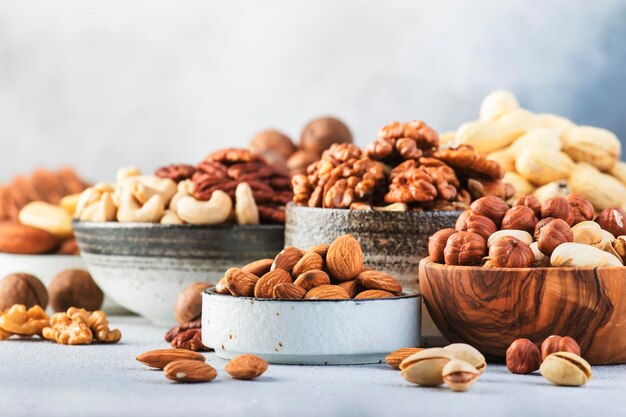
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are rich in healthy fats and antioxidants, which can support immune function.

Coping with Autoimmune Diseases
Living with an autoimmune disease can be challenging both physically and emotionally. It’s essential to seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends. Joining support groups or online communities can provide a valuable platform to share experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing autoimmune diseases require a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of living with these conditions. By taking proactive steps, seeking medical guidance, and making positive lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage their autoimmune diseases and lead fulfilling lives.